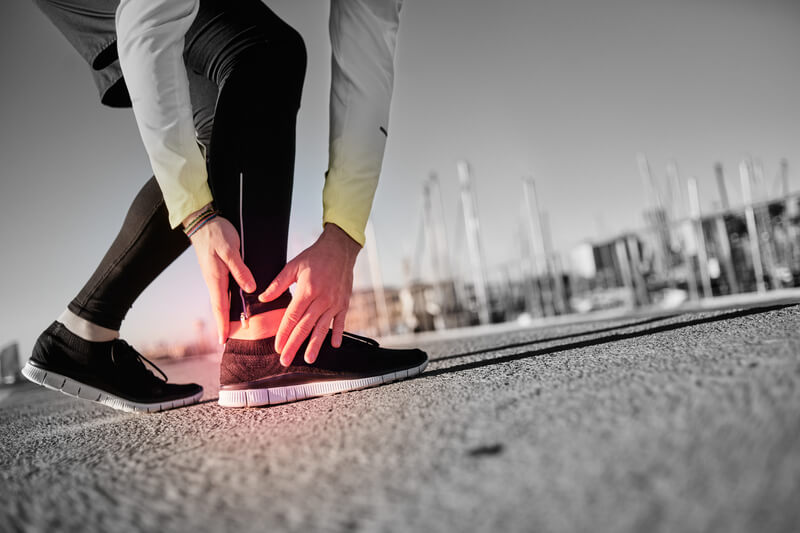

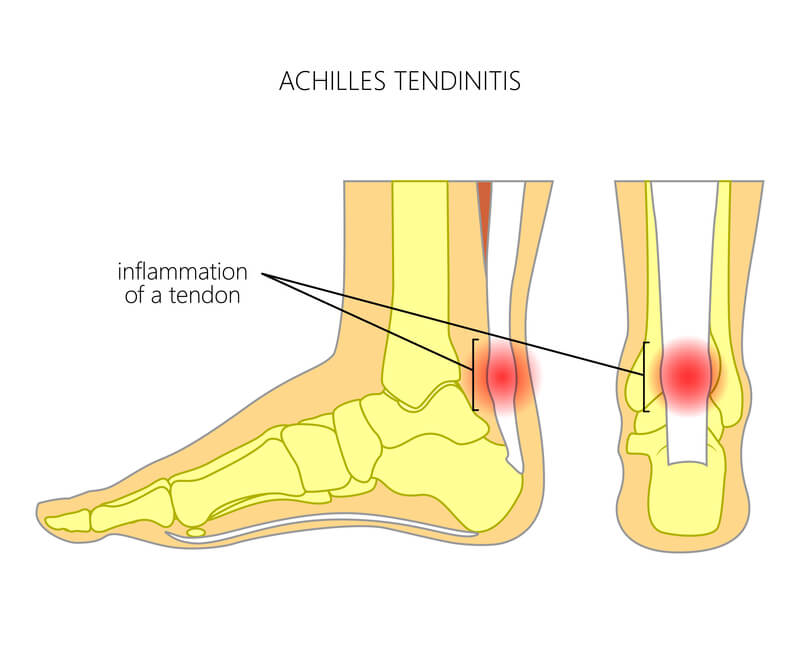
Achilles tendonitis is a common injury among athletes, particularly runners. The Achilles tendon connects your calf muscle to the heel and is the largest tendon in the body.
Since the Achilles tendon is used for numerous day-to-day activities, such as walking, running, climbing, and jumping, it is susceptible to injury and inflammation (Achilles tendonitis).
At Advanced Foot & Ankle Wellness Center, foot and ankle specialist, Dr. Melissa Wawrzynek, has extensive experience treating Achilles tendonitis.
What are the primary causes of Achilles tendonitis?
Overuse and placing too much stress on the tendon are the leading causes of Achilles tendonitis. Generally, the most significant risk factor for Achilles tendonitis is the sudden increase in intensity and frequency of exercise. This can result in the tightening of your calf muscles and result in Achilles tendonitis.
It is, therefore, essential to avoid unnecessary stress on the Achilles tendon. When you start exercising, you want to increase your activity gradually, not suddenly. This allows your body to adjust to your new level of activity.
When working out, it is also important to maintain your flexibility. Stretch your calf muscles before exercising to reduce the stress on the Achilles tendon.
Additionally, bone spurs (excess bone growth where the Achilles tendon attaches to the heel) can rub against the tendon and contribute to Achilles tendonitis.
What are the primary symptoms of Achilles tendonitis?
When you suffer from Achilles tendonitis, you experience pain along the back of your heel, where the Achilles tendon is located.
The pain tends to increase the more you are active. If you exercise, the pain generally worsens the day after. When you wake up in the morning, you may also feel pain and stiffness near the Achilles tendon.
If you feel or hear a pop at the back of your heel, that means that your Achilles tendon has torn, and should seek immediate medical attention.
What are the different categories of Achilles Tendonitis?
There are three different categories of Achilles tendonitis, including paratenonitis, insertional, and non-insertional.
Paratenonitis
Paratenonitis, also known as tenosynovitis, is an inflammation of the paratenon. The paratenon is the outer coating of the Achilles tendon. This condition most often impacts runners. Painful adhesions between the Achilles tendon and the outer lining occur with Paratenonitis.
Insertional Achilles Tendonitis
Insertional Achilles Tendonitis occurs at the point where the Achilles tendon attaches to the heel. Insertional Achilles tendonitis is usually caused by overuse. However, certain deformities or anatomic variances can make an individual more likely to develop Achilles tendonitis.
A bony protrusion like a heel spur, Haglund’s deformity, or a square-backed heel is all anatomic variances that can result in someone having a higher risk of developing Achilles tendonitis. All of these anatomic variations result in the bone rubbing against the tendon.
With Insertional Achilles tendonitis, the small fluid-filled sac at the back of the heel, known as the bursa, can also become inflamed. The bursa helps to reduce friction between the bone and soft tissues. If the Achilles tendon becomes tight, that can result in a traction injury, resulting in more bone spurs on the back of the heel.
Noninsertional Achilles Tendonitis
Noninsertional Achilles Tendonitis impacts the middle portion of the Achilles tendon. It generally occurs about 4-6 cm above where the Achilles tendon inserts at the heel.
This region is known as the “watershed region” of the Achilles tendon. This area doesn’t heal as quickly as it has a poor blood supply.
Noninsertional Achilles tendonitis is a degenerative condition. The fibers tend to tear and fray over time. This causes the tendon to begin to thicken, resulting in significant pain.
What are the treatment options for Achilles tendonitis?
The type of treatment you need for your Achilles tendonitis depends on the category of your injury. Our foot and ankle specialist at Advanced Foot & Wellness, Dr. Melissa Wawrzynek, will examine you and create a treatment plan.
Nonsurgical Treatment
With Achilles tendonitis, the initial treatment plan leans more toward the conservative. Oral anti-inflammatory medication can be used to reduce pain and swelling, as well as topical medications as well as shockwave therapy.
If you have paratenonitis, physical therapy is beneficial. Rest is often recommended as well. If rest and physical therapy don’t relieve the symptoms, Dr. Melissa Wawrzynek may recommend shockwave treatment.
This treatment plan is used to break up adhesions. It is highly effective as well at relieving pain.
With insertional Achilles tendonitis, the initial treatment usually involves rest, ice, compression, elevation, stretching, and physical therapy. Another effective treatment is high-energy ultrasounds.
Noninsertional Achilles Tendonitis can be treated with physical therapy and eccentric stretching. Eccentric stretching is something that is done under the supervision of a qualified physical therapist.
It involves contracting and tightening the Achilles tendon as it lengthens. This procedure has to be done with professional supervision to ensure that further damage to the tendon does not occur.
Acellular Amnion-Derived Allograft injections work for both insertional and noninsertional Achilles tendonitis. This amniotic membrane allograft uses donated placenta obtained via Cesarean delivery. It retains the beneficial intrinsic properties of the amniotic membrane, which include collagen, hyaluronic acid, and growth factors.
The natural properties of the allograft provide protection, lubrication, and tissue support. It is regenerative medicine, not stem cell therapy. This natural solution is injected into the Achilles tendon to promote healing.
As long as the Achilles tendon hasn’t ruptured, a plantarflexion cast is a common treatment, as long as the tear is detected right away and there is no gaping in the tendon. A plantarflexion cast has to be worn for around 8 weeks.
If there is a gap in the tendon or the tear is not detected right away, surgery is often recommended.
Surgical Treatment
Surgical treatments are considered if nonsurgical treatments fail. At Advanced Foot & Ankle Wellness Center, Dr. Melissa Wawrzynek is skilled at performing Achilles tendon procedures when necessary.
Surgical treatment often involves the removal of the damaged tissue or debridement. If there are heel spurs, they generally are removed as well. Any damage to the tendon is then repaired.
With insertional Achilles tendonitis, where the tendon is detached from the insertion point at the heel, the damaged tissue is removed and the tendon is reattached and repaired.
When the Achilles tendon is torn, surgical repair is usually required. Surgical repair ensures that the torn Achilles tendon heals at the correct length. There are different surgical approaches to repairing the Achilles tendon, including minimally invasive techniques that use smaller incisions that have lower rates of complication as compared to open procedures.
Typically, patients begin weight-bearing within 6 weeks of surgery. After that, physical therapy is a vital part of the recovery process. Surgery for Achilles tendonitis is usually successful for a vast majority of patients.
Dr. Melissa Will Help Get You Back On Your Feet
Dr. Melissa Wawrzynek is a board-certified foot and ankle specialist and offers a broad range of advanced orthopedic, sports medicine, and regenerative treatments.
Our doctor and her team will consult with you regularly to ensure you return to health and receive the highest quality care.
If you’re ready to return to full speed as quickly, easily, and safely as possible, schedule an appointment today.

